Raspberry Pi Homelab - Part 1 - ArgoCD
managing continuous delivery with ArgoCD & k3s
· 4 min read
Introduction #
You can find all of the manifests for my k8s setup at my homelab GitHub repository.
Over the past few weeks I have been playing around with my RaspberryPi 5 to host a k3s cluster, a Certificate Authority, some microservices and to learn physical computing.
It’s been going pretty well, but I wanted to minimize the amount of manual intervention needed from me to deploy and debug services running in my k3s cluster. Since I have had experience with ArgoCD, I knew it was a good tool for the job!
The ultimate goal is to get the cluster up and running on my Raspberry Pi and be able to securely access it not only from my home network but also anywhere in the world (thanks to Tailscale! - more on it on another post).

One Node Home Server - Raspberry Pi 5
K3s #
My Raspberry Pi kubernetes cluster runs on a k3s distribution, which is packaged as a single <70MB binary. Perfect for my use case!
Following the docs, to get a k3s cluster up and running on my 1 node RaspberryPi cluster all I need to do is run:
Add cgroup_memory=1 cgroup_enable=memory to the end of /boot/firmware/cmdline.txt
sudo rebootcurl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -ArgoCD #
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. It’s an amazing project with a large active community! I encourage you to head over to the docs to learn more if you’re interested!
How I bootstrap ArgoCD #
I personally pick the version of ArgoCD I want to deploy on my cluster and run:
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/<VERSION>/manifests/install.yamlThis installs a non-HA version of Argo, which is ok for my homelab setup.
Once I get Argo running in the cluster and the pods come up and healthy, I log into the UI with the initial admin login and make sure it’s properly responding:
argocd login --core
argocd admin initial-password # copy the password
argocd admin dashboard # username: admin / password copied from aboveManaging Applications #
In short, ArgoCD reacts to changes in version control systems and applies changes to Kubernetes objects in cluster(s).
There are a variety of ways that you can structure repositories to manage applications. For the purpose of this guide we will have of repository called homelab that will both host the ArgoCD applications and the configuration of those apps.
I encourage you to read this post by Kostis Kapelonis on different ways to structure your Git repos.
App-of-Apps Pattern #
In order for us to avoid having to kubectl apply -f each application individually, we will leverage the app-of-apps pattern through a root application. One of the main goals was to manually intervene as little as possible!
The application YAML will point to the k8s/apps folder which will apply all applications in the cluster for us auto magically.
Root Application #
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
name: root
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: argocd
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
path: k8s/apps
repoURL: https://github.com/rafaelbroseghini/homelab.git
targetRevision: HEAD
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueWe need to manually bootstrap the root application once and only once:
kubectl apply -f k8s/root.yamlManaging Applications #
Now that our root app is applied, it will start to apply its child resources immediatelly. Below is the argocd application that will get applied. That’s the power of ArgoCD! ArgoCD managing ArgoCD itself.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
name: argocd
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: argocd
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
path: k8s/config/argocd/base
repoURL: https://github.com/rafaelbroseghini/homelab.git
targetRevision: HEAD
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueI hope you can see how this process would repeat for any application(s) that you wish to deploy in your cluster.
We would add the Application yaml under the correct path in the apps folder and the root application will take care of auto syncing it for us!
Now head over to the ArgoCD UI /argocd path, and hard refresh your root application. You should see the argocd application show up and auto sync.
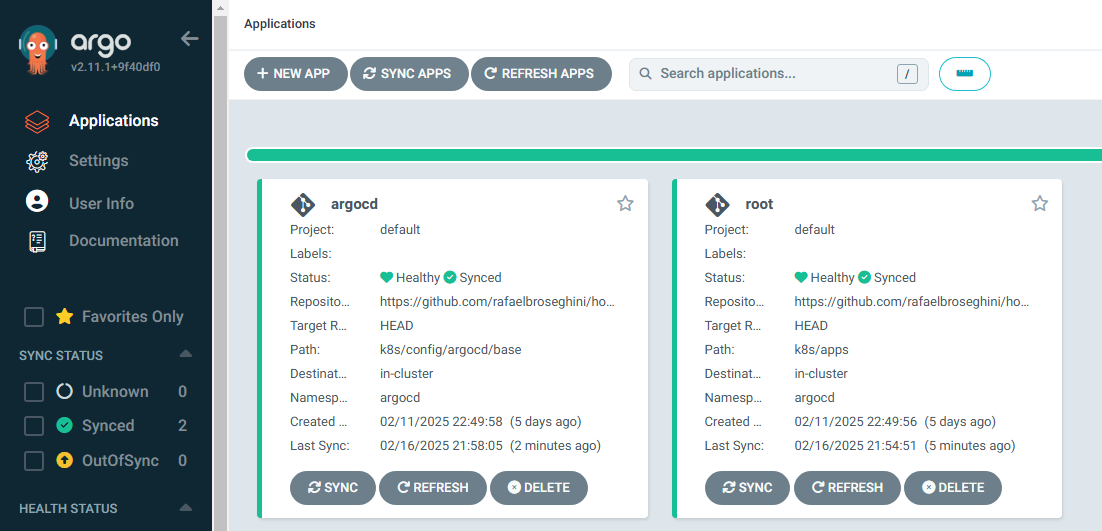
ArgoCD managing ArgoCD :-)
Using the structure at homelab/k8s allows me to manage a lightweight k3s cluster in my Raspberry Pi 5 with almost no manual intervention needed!
Feel free to clone the repo and play with it! :)